What effect does the interlayer material (such as PVB film) used in wired laminated glass have on the sound insulation performance? What are the differences between different types and thicknesses of sandwich materials on the final sound insulation effect? How to choose the suitable combination of materials to achieve the sound insulation effect?
The interlayer material (such as PVB film) in wired laminated glass has a significant impact on its sound insulation performance. Here are some key aspects and differences, and how to choose the suitable combination of materials for sound insulation:
Effect of sandwich materials on sound insulation performance
Material density and elastic modulus: The density and elastic modulus of a sandwich material determine its ability to absorb and block sound. High density and moderate elastic modulus help improve sound insulation performance.
Damping properties: The damping properties of a sandwich material determine its ability to absorb sound vibrations. Highly damped materials absorb the energy of sound waves more effectively, thereby reducing the transmission of sound.
Thickness of material: Increased thickness generally improves soundproofing properties because thicker materials are able to absorb and reflect more sound waves.
Differences in the final sound insulation effect of different types and thicknesses of sandwich materials
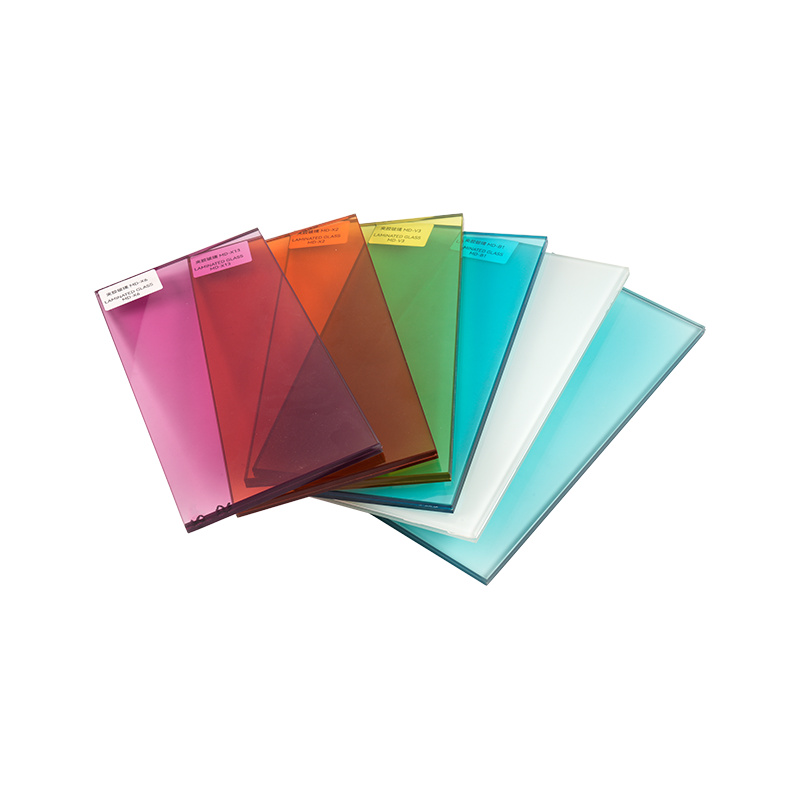
PVB (polyvinyl butyral):
Advantages: Commonly used sandwich material with good sound insulation properties and transparency.
Thickness effect: Increasing the thickness of the PVB layer can significantly improve the sound insulation performance. For example, a 0.76 mm thick PVB layer provides better sound insulation than a 0.38 mm thick layer.
SGP (SentryGlas Plus):
Advantages: Harder, higher-strength sandwich material than PVB, with higher sound insulation properties and greater safety.
Thickness effect: Although SGP is generally thinner than PVB, its hardness and high damping properties provide sound insulation.
EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer):
Advantages: Good weather resistance and moisture resistance, suitable for outdoor applications.
Effect of thickness: The sound insulation performance of EVA is directly related to its thickness. Increasing the thickness can improve the sound insulation effect, but its sound insulation effect is usually not as good as PVB and SGP.
Choose the suitable material combination for sound insulation
Determine application environment and requirements:
Building types: Residential buildings, commercial office buildings, concert halls, etc. have different requirements for sound insulation. Determining the application environment helps select the appropriate material.
Type of noise source: Determining the main noise sources (traffic noise, neighbor noise, industrial noise, etc.) and the frequency range of the noise (low, medium, high) can help select the most effective materials.
Consider overall performance:
Security: In places with high security requirements, such as banks, museums, etc., you may need to choose SGP with higher strength and anti-theft performance.
Light transmittance: For applications that require high transparency, such as display windows, showcases, etc., you can choose PVB with higher transparency or specific types of EVA.
Thickness combination optimization:
Double or multi-layer sandwich materials: Using a combination of double or multiple layers of sandwich materials of different thicknesses can further optimize sound insulation performance. For example, using two layers of 0.76 mm PVB sandwich material instead of a single layer of 1.52 mm PVB can absorb sound at different frequencies more effectively.
Practical application cases and tests
Conduct real-world application testing and simulations to evaluate the sound insulation effectiveness of different material combinations. For example, install prototypes in the lab or in the field and use sound level meters to measure the sound insulation performance of different combinations to ensure that the materials chosen meet the sound insulation needs of the specific application.
Through the above methods and considerations, the suitable combination of wired laminated glass materials can be selected to achieve the sound insulation effect while taking into account other performance requirements.




 中文简体
中文简体